A hosts file is a plain text file used by many operating systems to map hostnames (such as www.humanextended.com) to IP addresses (such as 63.250.43.134). Today, the vast majority of mapping is performed by the global domain name system (DNS), but the hosts file still exists on Windows as a local override.
The hosts file contains one mapping per line. Each line specifies an IP address, then at least one space, and then the hostname to be mapped to that IP address. Here is an example:
0.0.0.0 ads.example.com
#
# Lines beginning with a hash (#) are ignored.
#
# If an app tries to resolve ads.example.com, it will get 0.0.0.0.
# This is an invalid address, so any connection attempt will fail.Ad blocking
You may wonder why anyone would use a hosts file instead of DNS. A common trick is to put advertising sites in the hosts file, causing the hostnames to resolve to an invalid address.
When an app downloads something from the internet, it typically connects to a host with using a friendly name such as ads.example.com or analytics.example.com. This name needs to be translated to an IP address so that a connection can be made.
Normally this is performed by DNS, which will return the IP address of the server. However, before DNS is checked, Windows checks the hosts file for any local overrides. If the host is mapped to 0.0.0.0, that will get returned to the caller, which will fail to connect. This is because 0.0.0.0 is forbidden as a destination address.
Unfortunately, this approach can be less-than-ideal:
- There may be many hosts used by the app, so you need to add each one.
- The lists of hosts used by the app can change with each update.
- If the app connects with IP directly, you cannot block with a hosts file.
Prerequisites
- You must be an administrator to modify the hosts file.
Instructions
- Open Notepad with Run as administrator
The hosts file is a protected system file. You must open your editor as an administrator in order to modify the file. On Windows, open the Start menu and type Notepad without hitting the enter key. Look for Run as administrator and click it.

- Press Control-O or click File > Open to open the dialog box
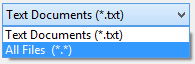
- In the lower-right corner, change Text documents (*.txt) to All Files (*.*)
If you don’t do this, the hosts file will not be visible. This is because the hosts file does not have a .txt extension.
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
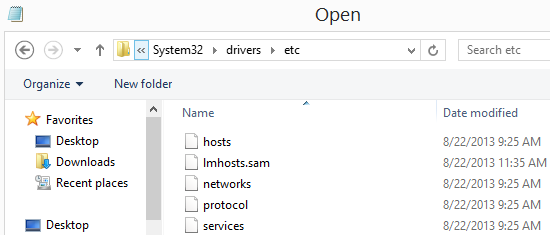
- Open the file named hosts
- Review comments
# A comment is a line that begins with a # (hash) symbol.
# Comments are ignored by Windows.
# You can write comments to explain why you made changes.
# There may be other comments that you should review. - Start a new blank line to add an entry
Each entry in the file must be on its own line. You can put the line anywhere.
- To add an entry, type the IP address, then at least one space, and then the host that should resolve to that IP address. To block a site, use 0.0.0.0 as the address
# Block www.example.com
0.0.0.0 www.example.com - Press Control-S or click File > Save to save the hosts file
Loopback address
You may also see online guides suggesting that you specify 127.0.0.1 as the IP address. This address is known as the loopback address and is essentially a reference to the same machine. However, using 0.0.0.0 is preferred because it will fail faster.
Reference
- 0.0.0.0 – Wikipedia – An article about the special IP address 0.0.0.0, which is prohibited as a destination IP address.
- localhost – Wikipedia – An article about
localhost, which is a special alias for the local computer. When you connect to localhost, you are connecting to your same computer.
Leave a Reply